Prostate Cancer
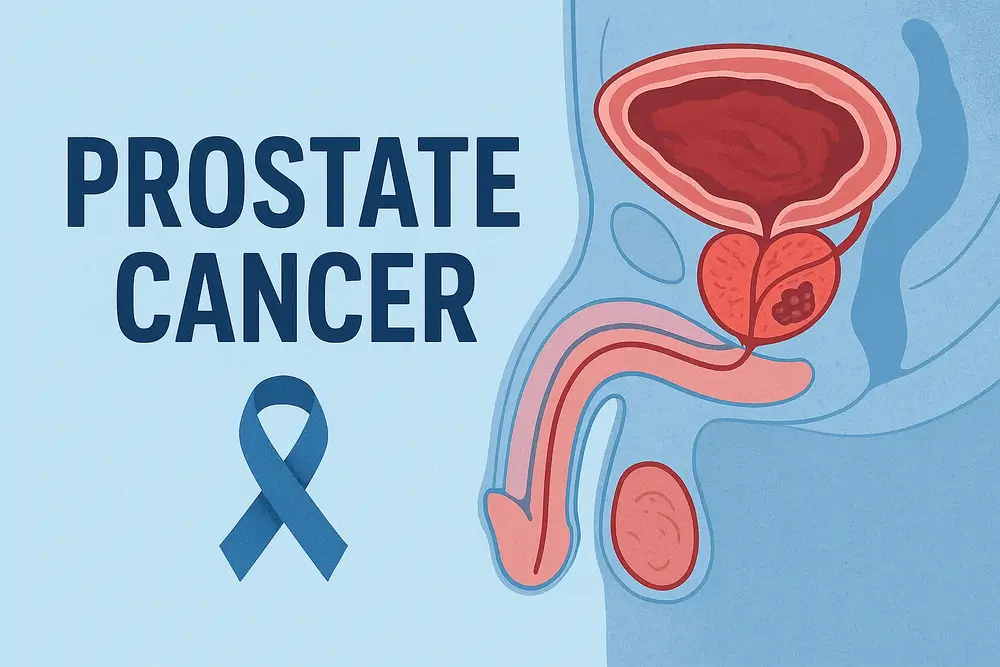
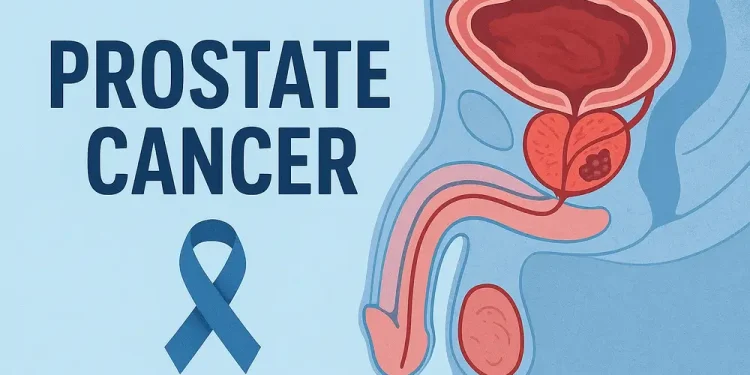
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers in men. It affects the prostate gland, a small organ that makes fluid for semen. This cancer usually grows slowly and stays in the prostate gland for a long time. However, some kinds of cancer grow slowly and may need only a little treatment, while others can be very aggressive and spread fast.
In this article, we’ll explore everything you need to know about prostate cancer, from its causes and risks to symptoms, treatment options, and prevention.
What is Prostate Cancer?
Prostate cancer occurs when cells in the prostate gland start to grow abnormally. The prostate is a tiny gland in men that is under the bladder and helps make some of the liquid in semen. When these cells change, they can grow into lumps called tumors. If these tumors are not taken care of, they can spread to other parts of the body, particularly the bones and lymph nodes.
Prostate cancer can be very serious in some cases, but not as much in others. Some men can have prostate cancer for a long time without any obvious signs, and it can grow slowly. This means that they may not require immediate treatment. On the other hand, there are situations where cancer grows fast and spreads rapidly, requiring immediate medical attention.
It’s important to find a problem early because it can help with getting better treatment. Getting regular check-ups and discussing any worries with a doctor can help find prostate cancer early, which can improve how well a person can be treated. It’s important to know about your health so you can make good decisions.

Causes of Prostate Cancer
The exact reason for prostate cancer is not completely known, but researchers think that several factors may play a role in causing the disease, including:
Genetic Mutations
Changes in the DNA of prostate cells can cause cancerous cells to grow. When cell growth and division are blocked it causes the cells to multiply uncontrollably, leading to this situation. As we get older, our bodies can naturally develop these mutations, or they can be caused by things like being around bad chemicals. Over time, if these mutated cells build up, they can create lumps called tumors. If not found and treated early, these tumors may turn into prostate cancer.
Hormonal Influence
Testosterone and other male hormones are important for the prostate to work properly, but they can also make prostate cancer grow faster. As men get older, changes in hormone levels can increase the chance of prostate cancer, even though these hormones help keep the prostate healthy. As men age, it’s important to monitor hormone levels because prostate cancer cells often depend on these hormones to grow. Talking to a doctor about hormone levels can help find any potential problems early.
Age
Prostate cancer is usually found in older men, specially those who are 50 years old and above. The risk of this condition increases as men get older, although it can also impact younger men. As time goes on, the cells in the prostate are more likely to change, which can sometimes lead to cancer. This is why doctors often advise older men to get checked regularly, so cancer can be found and treated early before it spreads.
Family History
If someone in your family, like your father, brother, or another close male relative, has had prostate cancer, then you are more likely to develop it as well. This means that prostate cancer may be passed down from family members, maybe because they have the same genes. If someone in your family has had the illness, it’s important to tell your doctor. You can talk about getting regular check-ups together to find any signs of cancer early, especially if there are other family members who have had it.
Ethnicity
African-American men have a higher chance of getting prostate cancer compared to men of other ethnicities, like white or Hispanic/Latino men. Furthermore, cancer is more likely to grow quickly in African-American men. Scientists are still trying to figure out why this happens, but it might be because of a mix of genetics, lifestyle, and the environment. It’s important for people in higher-risk groups to talk to their doctor about starting check ups early.
Symptoms of Prostate Cancer
In its early stages, prostate cancer often has no symptoms. As the cancer grows, symptoms may appear, which can include:
Weak urination or difficulties while peeing
Some men with prostate cancer have trouble beginning or ending urination. You may need to pee more often, specially at night, or your urine stream may feel weak. The symptoms occur because the cancer is putting pressure on the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder.
Blood in the urine or semen
Seeing blood in your urine or semen can be scary, but it could be a sign of prostate cancer. This symptom happens when cancer affects the tissues in the prostate or nearby areas. If you see any blood, it’s important to go to the doctor immediately.
Erectile dysfunction
Prostate cancer can affect the ability to get or keep an erection. If the cancer affects nerves or blood flow in the area, this could happen. Prostate cancer treatments, such as surgery or radiation therapy, can also cause erectile dysfunction as a side effect.
Discomfort in the pelvic area
Men who have prostate cancer may experience a dull pain or pressure in the lower part of the belly, known as the pelvic area. This feeling of pain can come from the cancer itself or when it spreads to nearby tissues. If you feel any strange pain or discomfort in this area, you should see a doctor.
Bone pain (if the cancer has spread)
If prostate cancer spreads to the bones, it can create pain in the hips, back, or other parts of the body. The pain in your bones may start off as not too bad, but it can get worse as the cancer gets worse. The amount of pain someone feels is based on how bad the cancer is and where it has spread in the bones.
Losing weight for no reason
Losing weight without trying could be a sign of advanced prostate cancer. This kind of weight loss occurs when the body is fighting a disease, and it can happen at the same time as other symptoms such as tiredness and not feeling hungry. If you see your weight changing suddenly, talk to a doctor.
Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer
Diagnosing prostate cancer usually involves a combination of tests, including:
Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test
This is a blood test that checks the level of a protein called PSA, which is made by the prostate. Higher PSA levels could indicate prostate cancer, but they might also be a result of other issues such as infections or a larger prostate. If your PSA level is high, your doctor may recommend more tests to determine if it’s because of cancer. Having PSA tests regularly can help find prostate cancer early when it’s easier to treat.
Digital Rectal Exam (DRE)
In this test, the doctor puts on a glove and uses lubrication to put a finger into the rectum to check the prostate gland. The aim is to look for anything unusual, such as lumps or hard areas, that could be a sign of prostate cancer. It’s an easy process that can find prostate problems early. Even though it might be uncomfortable, it’s a fast and helpful method for doctors to detect possible issues.
Biopsy
If tests such as the PSA or DRE indicate a potential problem, your doctor may suggest having a biopsy. This means using a needle to take small pieces of tissue from the prostate. The tissue is looked at with a microscope to see if there are cancer cells. A biopsy is the most certain method to diagnose prostate cancer and can help doctors choose the best treatment.
Treatment Options for Prostate Cancer
The way prostate cancer is treated depends on how fast it is growing and if it has spread beyond the prostate. Common treatment options include:
Active Surveillance
For prostate cancers with low risk, doctors may recommend monitoring the cancer instead of immediate treatment. This method is known as active surveillance. Regular appointments and PSA tests are necessary to keep an eye on how the cancer is progressing. Because certain prostate cancers grow slowly, it may not be necessary to have treatment right away, and waiting can help prevent side effects.
Surgery
A prostatectomy is a procedure to take out the prostate gland and nearby tissue through surgery. This is a usual treatment when the cancer hasn’t spread outside of the prostate. Doctors aim to eliminate the cancer by removing the prostate before it can grow or spread to other parts of the body.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses powerful rays to find and destroy cancer cells or reduce tumors. It may be the main treatment for prostate cancer or used after surgery to get rid of any remaining cancer cells. The aim of radiation therapy is to destroy cancer cells while preserving nearby healthy tissue. This treatment is made to be very accurate and can help control the cancer and increase the chances of getting better.
Hormone Therapy
Hormone therapy reduces the amount of testosterone in the body, which is necessary for prostate cancer cells to grow. It is commonly used when the cancer has extended outside the prostate or as part of a wider treatment strategy. This treatment slows down the growth of the cancer and sometimes makes the tumors smaller by lowering the amount of testosterone in the body.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a type of treatment that uses powerful medications to kill cancer cells all over the body. It is commonly used when prostate cancer has spread outside the prostate and requires more intense treatment. Chemotherapy can still help lessen symptoms and slow down cancer growth, even in the later stages. This helps people with advanced prostate cancer to have a better life by making it easier to manage and improving their quality of life.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy makes the immune system stronger in battling cancer. It is commonly prescribed to men with late-stage prostate cancer, particularly when other treatments are no longer effective. This treatment helps the body’s immune system recognize and fight cancer cells by making it stronger. Immunotherapy helps the body’s immune system get stronger so it can slow down cancer and fight it better.
Targeted Therapy
The use of targeted therapy involves the use of drugs that target particular weaknesses in cancer cells. It is commonly used for treating aggressive or advanced prostate cancers. Targeted therapy is more precise than chemotherapy because it only attacks the cancer cells, instead of all fast-growing cells in the body. Attacking these cells directly can slow down the cancer’s growth and can be more effective with fewer side effects than usual treatments.
Prevention of Prostate Cancer
While it may not be possible to prevent prostate cancer entirely, certain lifestyle changes can lower the risk:
Healthy Diet
A healthy diet may reduce the chance of getting prostate cancer. Make sure to eat lots of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy proteins such as chicken, fish, and beans. These foods have lots of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that can help to prevent cancer in your body. Reduce eating processed and high-fat foods because they can raise the risk. Instead, go for healthier fats such as the ones in nuts, seeds, and olive oil. Decrease the red and processed meats in your meals is a good idea too. You can keep your body strong and reduce the risk of getting prostate cancer by making these easy changes.
Regular Exercise
It is important to stay active to keep healthy and lower the chance of getting prostate cancer. Exercising regularly helps you keep a good weight, which is important because being overweight is connected to a greater chance of getting many types of cancer. You don’t need to do hard exercises to get the advantages. Just 30 minutes of walking, biking, or swimming each day can have a significant impact, even if its a light activity.
Exercise helps your body’s defense system, improves the way your blood flows, and regulates hormones that can impact cancer growth. It also supports mental well-being by reducing feelings of stress and anxiety. Doing a small amount of physical activity every day helps you stay healthy in the long run.
Avoid Smoking
Stopping smoking is really good for your health. Smoking doesn’t just hurt your lungs, but it’s also connected to worse types of prostate cancer. Smoking introduces harmful chemicals into your body and raises the chance of getting various types of cancer. Smoking can make cancer grow and spread faster. When you quit smoking, your body will begin to heal and reducing the chances of getting cancer, such as prostate cancer, will go down. You can always quit, no matter how late it is. Even if you’ve been smoking for a long time, stopping now can make you healthier and reduce the chances of getting very sick.
Regular checkups
It is important for men, especially those over 50 or with a family history of the disease, to get regular check-up for prostate cancer. Screening can find cancer early, when it is easier to treat. The most frequently used tests are a blood test called PSA (Prostate-Specific Antigen) and a digital rectal exam (DRE). Detecting cancer early can result in better results and might stop the cancer from spreading. If you have a greater chance of having a health problem because of your family history or other reasons, speak with your doctor about starting check up sooner. Having regular check-ups and talking to your doctor about your choices can help you take care of your health and avoid major problems.
Here are Some Resources for More Information
- Mayo Clinic – Prostate Cancer Risk Factors ( https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/prostate-cancer/symptoms-causes/syc-20353087 )
- WebMD – Prostate Cancer Guide ( https://www.webmd.com/prostate-cancer/default.htm )

In Last
Prostate cancer is a big health problem for lots of men, specially as they get older. Understanding the causes, risk factors, and symptoms can help men manage their health. It is important to also understand the various treatment choices available. Regular screenings are important for catching prostate cancer early so it can be managed effectively. This is key to preventing the disease from becoming more serious. If you are concerned about prostate cancer, it is important to have a conversation with your doctor. They can provide you with tips to prevent it and come up with a treatment plan that works best for you.
Choosing to eat healthy foods, exercise regularly, and avoid bad habits can reduce your chances of getting prostate cancer. Keeping up to date with information about the disease and taking these preventive measures can greatly help in keeping you healthy as you get older. It is important to prevent and be aware of prostate cancer in order to reduce the risks.