Intoxication
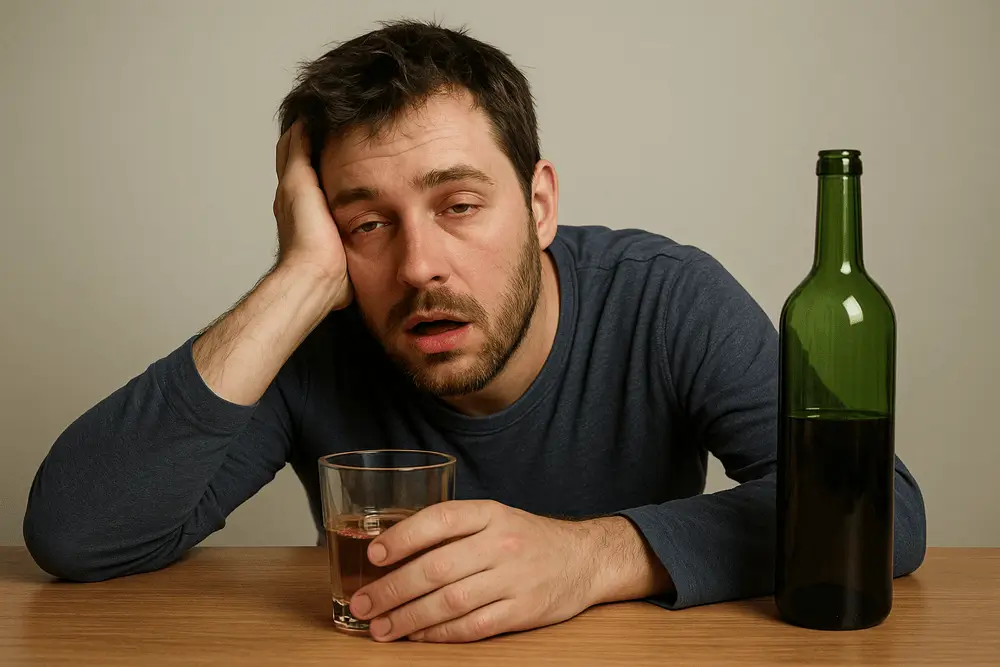

When someone’s mind and body are affected by substances like alcohol, drugs, or harmful chemicals, they are considered intoxicated. If a person uses too much of these things, it can mess with how their brain and nervous system function. This results in changes in their thinking, emotions, and behavior. For example, a person could feel mixed up, lightheaded, or very calm. They might struggle with walking, talking, or making good choices.
Other than alcohol, substances such as illegal drugs, medications, and toxins can also cause intoxication. Intoxication can happen fast and might cause someone to act differently, which can be risky. In extreme situations, it may result in long-term harm to a person’s health. It’s important to be mindful of what you consume and to get help if you have a habit of being intoxicated.
Causes of Intoxication
Alcohol
Alcohol is a frequent reason for people becoming intoxicated. Drinking too much can have a bad impact on a person’s brain and body. This can happen fast, specially if they consume a large amount in a short period. When you drink alcohol, it makes your brain work slower, which can cause you to speak unclearly, have trouble coordinating your movements, and make bad decisions. Adults can usually drink a little bit and be alright, but drinking a lot can cause major health problems like alcohol poisoning.
Drugs
Prescription and recreational drugs can both make you feel intoxicated. Using prescription drugs like painkillers or sedatives in a way that’s not prescribed by a doctor can make you feel intoxicated. Drugs like marijuana, cocaine, heroin, and synthetic drugs are very dangerous when used for fun. They can make it difficult to think, make you have very big changes in your emotions, and make you do risky things. Frequent use of these drugs can harm your health and cause dependence.
Toxins
Being around dangerous things like carbon monoxide, pesticides, or rotten food can also cause intoxication. Breathing in carbon monoxide from a broken heater can cause poisoning and lower the amount of oxygen in your body. Consuming food that is contaminated can lead to food poisoning, which can cause feelings of sickness, throwing up, and lack of strength. Preventing these issues can be achieved by making sure the environment is safe and food is stored properly to avoid toxins.
Medications
Certain medications, even common ones like cough syrup or pain relievers, can cause intoxication if taken in large amounts or combined with alcohol. Some people misuse medications to feel “high,” which is dangerous and can lead to serious side effects or overdose. Always follow the dosage instructions on medication labels and consult a doctor if you’re unsure about their safe use.
Symptoms of Intoxication
Mental Confusion or Inability to Concentrate
One of the first signs of intoxication is mental confusion. A person might struggle to think clearly or stay focused. They may forget what they were doing or have trouble following conversations. This happens because the substance affects how the brain processes information.
Drowsiness or Lack of Coordination
Intoxicated individuals often feel very sleepy or lethargic. They may also have trouble controlling their movements, making them appear clumsy. For example, walking in a straight line or holding an object might become difficult. This is because intoxication slows down the body’s responses.
Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea is another common symptom, especially with alcohol or drug use. The body reacts to the substance as if it’s a toxin and tries to get rid of it through vomiting. This can leave a person feeling weak and dehydrated.
Slurred Speech
When intoxicated, a person’s speech might become slow and difficult to understand. Words may be mumbled or slurred because the substances affect the muscles used for talking and the brain’s ability to control them.
Mood Changes (e.g., Aggression or Euphoria)
Substances can cause sudden mood changes. Some people may become overly happy and excited (euphoria), while others might become irritable or aggressive. These emotional swings can be unpredictable and depend on the type and amount of substance used.
Impaired Judgment and Decision-Making Abilities
Intoxicated individuals often make poor decisions. They may take risks they wouldn’t normally take, such as driving under the influence or engaging in unsafe behavior. This happens because intoxication affects the brain’s ability to think logically and assess situations.
Dizziness or Loss of Balance
A person might feel dizzy or unsteady while standing or walking. This can lead to falls or injuries. The loss of balance occurs because intoxication disrupts the body’s coordination system, which is controlled by the brain and inner ear.
Breathing Difficulties (in Severe Cases)
In severe cases, intoxication can slow down or even stop breathing. This is especially dangerous with substances like alcohol, opioids, or sedatives. Breathing problems are a medical emergency and require immediate attention to prevent life-threatening consequences.
Effects on Health
Short-Term Effects
Intoxication can lead to quick issues, specially if it affects decision-making and balance. For example, someone who is intoxicated might have car crashes if they attempt to drive because their ability to react quickly and focus are affected. Their balance problems can lead to accidents such as falls or injuries. And people who are intoxicated often do things that are dangerous, like having unsafe sex or getting into fights, which they wouldn’t usually do. These behaviors can have very bad outcomes, such as getting into trouble with the law or hurting themselves and other people.
Long-Term Effects
Repeated intoxication, especially from alcohol or drugs, can seriously harm the body over time. One common problem is liver disease, as the liver has to work hard to process toxins from substances. Over time, this can lead to conditions like liver damage or cirrhosis. Heart problems can also develop, such as high blood pressure or irregular heartbeats. The brain is also affected by long-term intoxication, potentially leading to memory problems, trouble focusing, or permanent brain damage. Addiction is another major long-term effect, as repeated substance use can make the body and mind dependent on it.
Mental Health Effects
Intoxication doesn’t just affect the body; it can also harm mental health. Prolonged or repeated use of alcohol or drugs is linked to mental health problems like anxiety and depression. These substances can change how the brain works, making it harder for people to manage their emotions. Over time, this can lead to conditions like paranoia, mood swings, or feelings of hopelessness. Memory loss is another common issue, especially in people who regularly use alcohol or drugs over a long period.
Organ Damage
The liver, kidneys, and brain are some of the most affected organs when it comes to long-term intoxication. The liver is often the first to suffer because it filters toxins out of the body. Chronic substance use can also damage the kidneys, leading to problems like kidney disease or failure. The brain is particularly vulnerable, as substances can disrupt its normal functioning, leading to permanent changes in thinking, memory, and mood.
Diagnosis of Intoxication
Diagnosing intoxication typically involves evaluating the person’s symptoms and behavior. Medical professionals will often ask about the substances the person may have consumed, including alcohol, drugs, or medications. The diagnosis is based on:
Physical Examination
When someone is suspected of being intoxicated, a doctor will often begin with a physical examination. This is important because it helps determine how the person is reacting to the substance and what immediate care may be needed. The doctor will check vital signs like heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing to see if they are in a safe range. Intoxication can cause these vital signs to be unusually high or low, which could be dangerous.
The doctor will also check for obvious signs of intoxication, like speaking unclearly or having trouble walking. The signs show that the substance has had an impact on the person’s ability to move and coordinate their body. Another thing they might see is confusion, where the person can’t answer questions right or remember basic facts. The doctor can quickly understand how serious the intoxication is by looking at these signs and decide what to do next for treatment.
Toxicology Tests
Toxicology tests are considered a dependable method for diagnosing intoxication. These tests assist doctors in determining the specific substance responsible for the intoxication. A doctor may use a blood test, urine test, or breath test to check for alcohol, drugs, or toxins in the body. These tests are particularly useful if the person cannot clearly tell what they have eaten.
For example, a breathalyzer test is often used to measure blood alcohol content (BAC) in suspected alcohol intoxication. If drugs are involved, urine or blood tests can detect specific drugs like marijuana, cocaine, or opioids. These tests are very accurate and can pinpoint what substance is affecting the person’s health. Identifying the substance is crucial because it helps doctors choose the most effective treatment.
Observation of Symptoms
Apart from doing physical exams and tests, doctors also rely on observation of symptoms to assess the severity of intoxication. Doctors look for specific signs like mood changes, such as becoming overly agitated, happy, or aggressive. These emotional shifts are common in people who are intoxicated by alcohol or drugs. Other symptoms they watch for include nausea, vomiting, or loss of coordination, which show that the body is reacting to the substance in a harmful way.
Doctors will pay attention to the person’s behavior, checking if they can respond to questions or follow simple instructions. If a person is too confused or unable to function normally, it suggests a higher level of intoxication, and the doctor will act quickly to help manage the situation.
Mental Health Assessment
Sometimes, intoxication is linked to long-term substance abuse, and a mental health assessment may be needed. This step is particularly important for people who have a history of using alcohol or drugs. The doctor may ask questions about the person’s mood, thought patterns, and behaviors. They will look for signs of addiction, such as frequent substance use, cravings, or withdrawal symptoms.
In severe cases of intoxication, the person may need to be hospitalized for close monitoring. Medical professionals will regularly monitor the person’s heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing to make sure they are stable. If they are very thirsty or in trouble, they may get a tube in their arm to put fluids into their body and balance the salts in their body. The person needs to go to the hospital to stay safe, especially if their condition could get worse or if they are having trouble breathing or staying awake. While staying at the hospital, doctors are able to promptly address any serious dangers to health.
Activated Charcoal
When intoxication is caused by swallowing toxins or harmful substances, doctors might use activated charcoal. This substance functions by catching toxins in the stomach and stopping them from getting into the blood. It’s usually given shortly after the poison is ingested because it works best within the first couple of hours. This therapy helps lessen the harmful substance in the body and lowers the chance of more harm. Activated charcoal is often used in poisoning cases and it is considered to be a safe method.
Oxygen Therapy
If someone has breathed in carbon monoxide or is having trouble breathing because they are intoxicated, they might need to get oxygen therapy. This means giving pure oxygen through a mask or nasal tube to help the blood get normal levels of oxygen again. Carbon monoxide poisoning stops oxygen from getting to the body’s organs, which can be very harmful. Doctors can assist the body in getting better and lower the chance of lasting harm to the brain and other organs by providing oxygen. Oxygen therapy is a basic but life-saving treatment for breathing problems.
Treatment for Alcohol Intoxication
For mild to moderate alcohol intoxication, the person is typically advised to rest and hydrate. Serious cases of alcohol poisoning, however, require emergency treatment, including:
Rest and Hydration
For mild to moderate alcohol intoxication, the best treatment is to allow the body time to process the alcohol. The person should rest in a safe, quiet place and avoid consuming more alcohol. Drinking plenty of water or electrolyte drinks can help prevent dehydration caused by alcohol. Light snacks may also help stabilize blood sugar levels. Rest and hydration support the body’s natural ability to recover from intoxication.
IV Fluids
In serious cases of alcohol poisoning, IV fluids may be given in a hospital to rehydrate the body quickly. Alcohol can cause dehydration by increasing urine production, which can upset the balance of electrolytes in the body. IV fluids help restore lost fluids and nutrients, which is essential for stabilizing the person’s condition. This treatment is particularly important for people who are too ill to drink fluids on their own.
Benzodiazepines